🤬
angr 바이너리 분석 활용 방안 3
August 14, 2020
angr fauxware 문제 풀이
문제 바이너리 dnsdudrla97/angr-doc
data 섹션
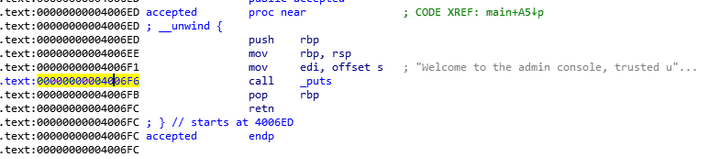
authenticate 함수
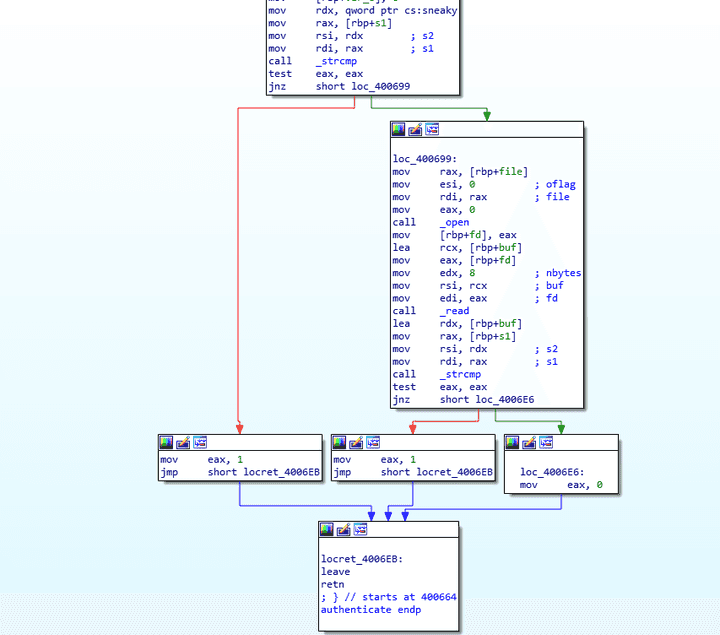
sneaky전역 변수가 가리키고 있는 문자열 과 유저 이름을strcmp함수를 바탕으로 비교를 통해 같으면 1을 반환하고 아닐시 유저 이름에 해당 하는 파일 이름을open함수를 바탕으로 읽고 해당 값과 유저 패스워드와 비교하여 같으면 1을 반환 아니면 0을 반환한다.- 우리가 피해야할 주소 값은
0x4006E6임을 알 수있다.
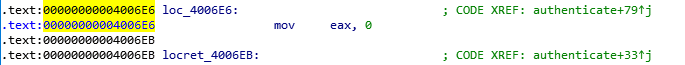
접근해야 하는 위치
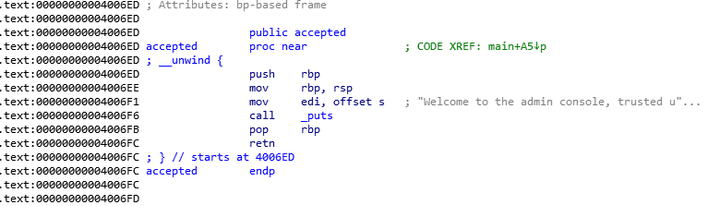
- 기본적으로 앞에서
authenticate함수에서 반환된 값이 1 일 경우accepted함수를 호출하게 된다.
angr solve 1
def solve2():
p = angr.Project('./fauxware', auto_load_libs=False)
state=p.factory.entry_state()
sm=p.factory.simgr(state)
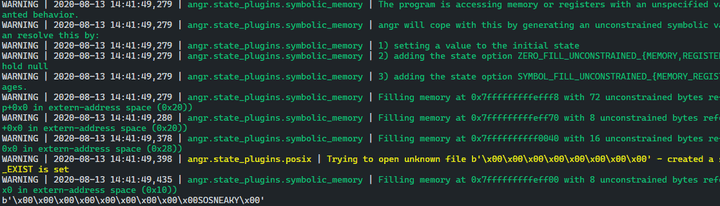
sm.explore(find=0x4006F6, avoid=(0x4007CE, 0x4006E6))
print(sm.found[0].posix.dumps(0))
angr sovle 2
def solve1():
p = angr.Project('./fauxware', auto_load_libs=False)
state = p.factory.entry_state()
sm = p.factory.simgr(state)
sm.run(until = lambda sm_: len(sm_.active) > 1)
input_0 = sm.active[0].posix.dumps(0)
input_1 = sm.active[1].posix.dumps(0)
r = None
print(input_0)
print(input_1)
import angr
import sys
def bse():
# 먼저 바이너리를 Angr 프로젝트에 로드 한다.
p = angr.Project('./fauxware', auto_load_libs=False)
# entry_state 프로그램의 진입점에서 가능한 프로그램 상태를 매우 일반적인 표현인 SimState로 생성한다.
state = p.factory.entry_state()
# SimulationManager는 단지 그것들을 관리하기 위한 많은 편리한 인터페이스가 부착된
# 다양한 태그를 가진 상태들의 모음이다
sm = p.factory.simgr(state)
# 실행 시작-> 두 가지 모두 만족할만한 분기 문에 도달할 때 까지
# 프로그램을 실행 한다. 현재 active 주소 값이 1 보다 클때 까지
sm.run(until = lambda sm_: len(sm_.active) > 1)
# 입력 조건
input_0 = sm.active[0].posix.dumps(0)
input_1 = sm.active[1].posix.dumps(0)
r = None
print(input_0)
print(input_1)
if __name__ == "__main__":
bse()